















EZPZ Accounting: Your Partner in Hassle-Free, Comprehensive Accounting Solutions
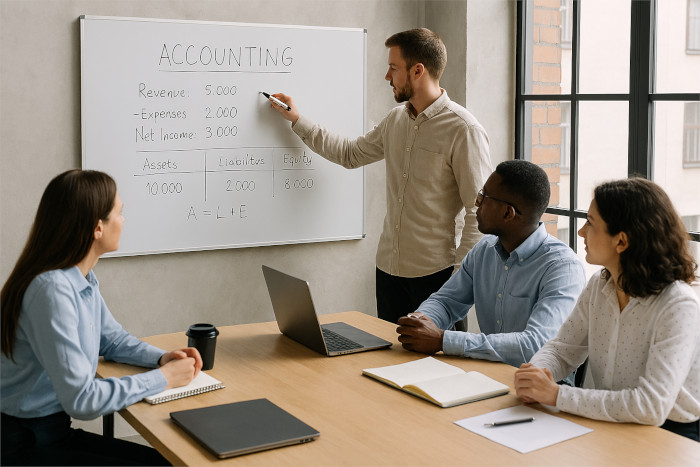

At EZPZ Accounting, we provide a dedicated, high-quality team focused on delivering tailored accounting solutions with maximum efficiency to meet your business's unique needs.
- Complete accounting system setup from scratch.
- Support for your in-house accounting team.
- Full-service outsourced accounting.
Our dedication to hassle-free service, top-quality work, quick turnaround, and competitive pricing makes us the ideal partner for your accounting needs, regardless of the software you currently use.
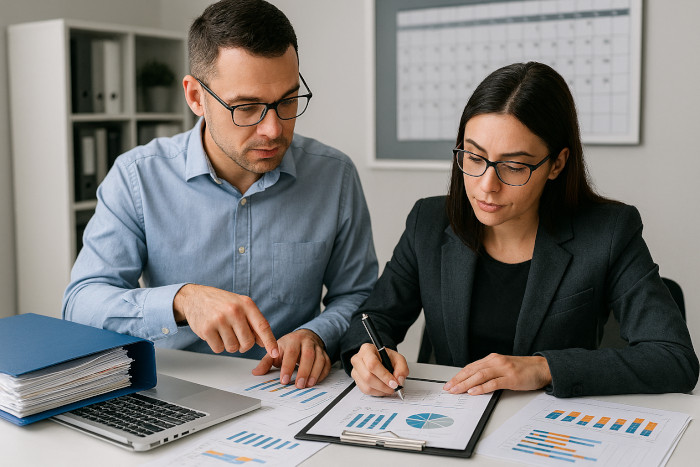

Our experienced team is also skilled at bringing out-of-date records current, so you never have to worry about missing a deadline or dealing with outdated financial data.
Why Choose EZPZ Accounting?
American standards and systems with the Filipino heart and brilliance!
We offer a range of services and benefits that set us apart in the industry, ensuring that your accounting needs are met efficiently and professionally. Here’s why we’re the best choice for businesses in Residential, Retail & Commercial Property Management, Facility Management Firms, Real Estate Developers, Building Contractors, Architecture & Engineering Firms, Healthcare Facilities, and Senior Living Communities:
In-House Team and Quality-Controlled Workflows
At EZPZ, our in-house team of bookkeepers, accountants, and controllers ensures precision and accountability on every accounting project. We use advanced project management systems to streamline workflows and guarantee timely, accurate results. With thorough oversight at every stage, we simplify complex accounting into a hassle-free, efficient experience tailored to your needs.

Secure Data and Processes
We understand the importance of security in handling sensitive financial data. We have experience with robust security protocols to protect your data and ensure secure processes from start to finish. Our standards and knowledge safeguards your information, keeping your finances confidential and compliant with industry standards.

Comprehensive Insurance Coverage
Your peace of mind is our priority. EZPZ Accounting is fully insured with coverage that includes Errors and Omissions, Crime and Fraud, and Professional Liability Insurance. This ensures that we are protected in all aspects of our business, so you can trust that your accounting is in safe, capable hands.

Easy and Comprehensive Client Onboarding
We believe that great service begins with seamless client onboarding. Our team works closely with you to ensure quick and easy access to your accounting platform and data repository. We also conduct a thorough briefing session to fully understand your unique accounting processes, so we can tailor our services to fit your business perfectly.

Transparent & Efficient Communication
At EZPZ, we keep you informed every step of the way. You’ll receive daily or weekly email briefings detailing our progress and any clarifications we need, giving you complete visibility into your accounting status. We also provide regular financial reports as required, so you always know where your business stands financially.
Affordable, Reliable, and Comprehensive Accounting Services
We understand the importance of affordability without sacrificing quality. Our services are competitively priced, allowing you to get the most value for your money while benefiting from professional accounting solutions.
Let EZPZ Accounting be your go-to partner for all your accounting needs. From supporting in-house teams to full outsourcing and everything in between, we provide end-to-end services that help you stay compliant, secure, and up to date.
Ready to Transform Your Accounting Experience?
Let EZPZ Accounting take the stress out of managing your finances, so you can focus on growing your business. Contact us today to learn how we can help streamline your accounting and bring your financial management to the next level.
Schedule Appointment
When your Accounting
Delivers the Reports
Co-Founder Tom Barrett will translate your numbers into the story that is setting your financial trend. Can you cut costs? Where are your profits maximized? Are you paying too much in departments? What’s your breakeven? What’s the best tax strategy? Do you have monthly Budgets?

When you Understand
your Profits
Founder Peter Jorgenson will help you see outside the box. Do you understand your offer in the marketplace? What is your target market? Are you thinking niche enough to expand from realistically? What tech stack is best for you? Do you know your CPA (cost per acquisition)?

EZPZ wants to Join your
Winning Team
Incredible things in the business world are never made by a single person but by a team.
We are here to support your accounting team the way it best serves your existing framework. Whatever accounting system you use, we will train our bookkeepers to fit within your company. Our professional staff is at the ready for fresh ideas. When you are ready to scale, we are prepared to grow with you.

When you are Ready for a
“Breakout Move.”
Conformity is the jailer of freedom and the enemy of growth.
Our strategy is to grow with you. We want to support you where you are at now. Provide financial expertise to make good growth decisions with minimal cost and risk. Advice on innovative, technically scalable solutions to grow your company. And match you with the right marketing partners that fit you.